low end tidal co2 during cpr
Goal is 10 mmHg during CPR. The maximum value of CO 2 at the end of the breath is designated as end-tidal partial pressure of CO 2 PETCO 2.

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training
Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO.

. Non-invasive assessment of fluid responsiveness by changes in partial end-tidal CO2 pressure during a passive leg-raising maneuver. The available studies provided consistent but low-quality evidence that ETCO2measurements 10mmHg obtained at various time points during CPR are substantially related to ROSC. The slope and the height of phase III is dependent on the CO 2 concentration of alveoli and their emptying patterns.
Disclosed is a nasal ventilation mask having separate ports to monitor end-tidal CO2 expulsion integrated into the mask in order to monitor end-tidal CO2 expelled nasally or orally. Also disclosed is a CPR mask for nose-to-mouth andor mouth-to-mouth resuscitation having a body shaped to cover the nose andor mouth of a victim said mask including a CO2 absorber for. Low end tidal co2 during cpr Wednesday April 6 2022 The first sign of the return of spontaneous circulation ROSC during CPR is increase in ETCO2.
N Engl J Med. Low ETCO2 below 10 mm HG may be caused by either poor compression technique or from low perfusion and metabolism after a long downtime or shock despite good compressions. Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for confirming tracheal tube placement assessing the effectiveness of chest compressions predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC.
This pattern not previously described is different from that observed in animal and adult cardiac arrest caused by ventricular fibrillation during which ETCO2 decreases to almost zero after the onset of arrest begins to increase after the onset of effective CPR and increases to. During CPR the blood flow to the lung may be so low that few alveoli are perfused. End-tidal CO 2 monitoring during CPR is a relatively new area in which research is ongoing.
Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC. Thus ETco 2 monitoring is a noninvasive way to measure coronary artery blood flow and return of spontaneous circulation during CPR. Therefore the ETCO 2 is low.
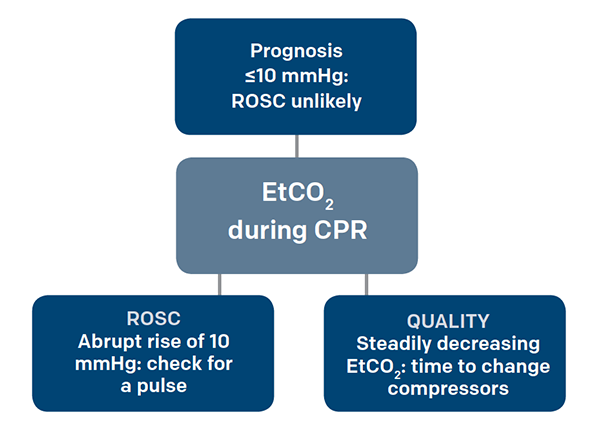
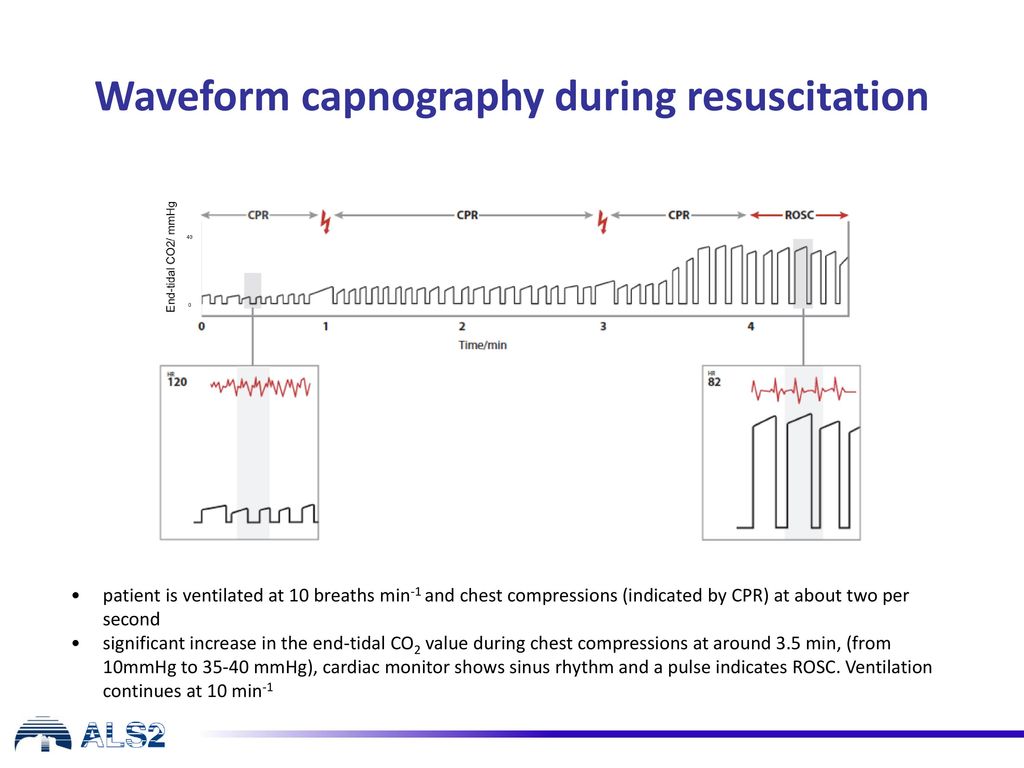
This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. End-tidal carbon dioxide.
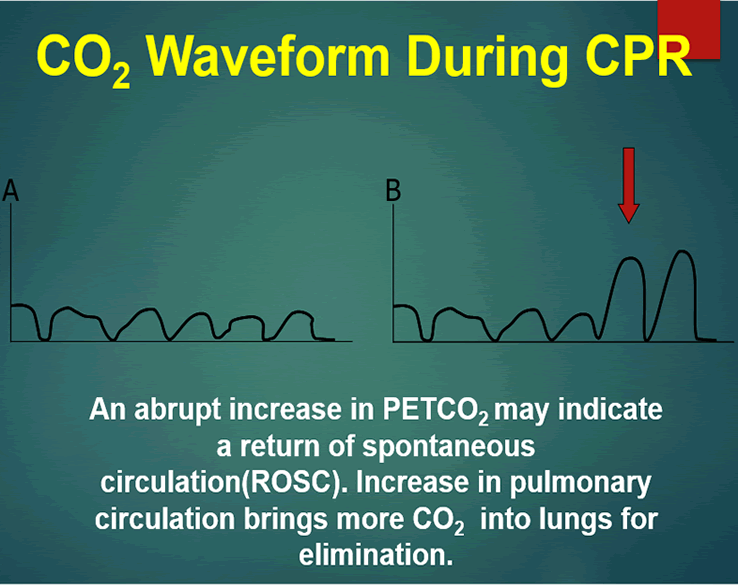
Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 identification of ROSC. Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check ETCO2 at 20 minutes of CPR is prognostically useful.
After 20 minutes of CPR death occurs if ETCO2 is consistently below 10 mmHg with 100 sensitivity and specificity 15. Expect it to be as high as 60 mmHg when ROSC is achieved. During CPR ETCO2 levels were initially high decreased to low levels and increased again at ROSC.
Initial ETCO2or 20-min ETCO220mmHg appears to be a better predictor of ROSC than the 10mmHg cut off value. It is generally lower than arterial partial pressure of CO 2 PaCO 2 by about 5 mmHg in healthy subjects. Low etCO2 may be due to suboptimal CPR technique but it may also be due to death cessation of cellular respiration leading to a lack of CO2 production.
Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector. Another use of ETco 2 monitoring is during procedural sedation and analgesia PSA. Systematic review and meta-analysis of end-tidal carbon dioxide values associated with return of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Since tidal volumes delivered with a bag-valve device are high many alveoli are ventilated but not perfused. ETCO2 is a reliable indicator with a high prognostic value in determining the CPR outcome 11 12.
Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. Rounded low rectangle EtCO 2 waveform during CPR with a high spike on ROSC. J Intensive Care Med.
PaCO2 PetCO2 End tidal measurement from expired or exhaled air PaCO2 Arterial blood gas sample End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation. A rapid rise in EtCO 2 during CPR can indicate ROSC due to the improved oxygen delivery. Studies have shown that in patients who had ETCO2 of 10 mmHg or less cardiac arrest was associated with death 13 14.
Additional cut-off values were also found. Pintado R Pérez Madueño V Díaz Monrové JC. 4 to 5 CO2 PetCO2 vs.
Evidence suggests a persistently low ETco 2 value and a widened Paco 2-to-ETco 2 gradient during CPR are associated with poor outcomes. Free Full Text Critical Care.

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Graphic Recordings Of Aortic Pressure Aop Air Flow And End Tidal Download Scientific Diagram

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Wendy Blount Dvm Cpr Update Recover Ppt Download
Cpr Mobile Code Stand With Capnograph Capnography
Waveform Capnography Version Jan Ppt Download

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation
